Tutorial Library
Learning Point
introduction of computers

What Is a Computer?
In the simplest terms, a computer is a machine that accepts some kind of input, performs actions and calculations according to a set of instructions, and returns the result of its calculations. The term "computer" was originally given to humans (human computers) who performed numerical calculations using mechanical calculators, such as the abacus and slide rule. The term was later given to a mechanical device as they began replacing the human computers.
Charles Babbage is called the "Grand Father" of the computer. The First mechanical computer designed by Charles Babbage was called Analytical Engine. It uses read-only memory in the form of punch cards.
In simplest terms we can say that a computer is an electronic machine which helps in solving problems quickly and easily. It solves problems according to instructions given to it by the computer user called programs or software. It is a digital machine(that uses binary digits) used in all fields.
All computers, regardless of their size, purpose, or type, follow this definition. Modern computers are very different from early computers. They can do billions of calculations per second. Most people have used a personal computer in their home or at work. Computers do many different jobs where automation is useful. Some examples are controlling traffic lights, vehicle computers, security systems, washing machines and digital televisions.
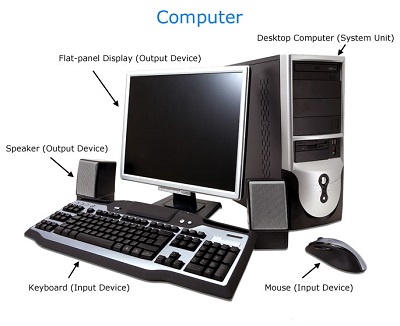
Computer is an advanced electronic device that takes raw data as input from the user and processes these data under the control of set of instructions (called program) and gives the result (output) and saves output for the future use. It can process both numerical and non-numerical (arithmetic and logical) calculations.
What is the full form Computer?
C = Commonly
O = Operating
M = Machine
P = Particularly
U = Used for
T = Technical and
E = Educational
R = Research.
Computer Classification: By Size and Power:
Computers differ based on their data processing abilities. They are classified according to purpose, data handling and functionality.
According to functionality, computers are classified as:
• Analog Computer: A computer that represents numbers by some continuously variable physical quantity, whose variations mimic the properties of some system being modeled.
• Personal computer: A personal computer is a computer small and low cost. The term "personal computer" is used to describe desktop computers (desktops).
• Workstation: A terminal or desktop computer in a network. In this context, workstation is just a generic term for a user's machine (client machine) in contrast to a "server" or "mainframe."
• Minicomputer: A minicomputer isn't very mini. At least, not in the way most of us think of mini. You know how big your personal computer is and its related family.
• Mainframe: It refers to the kind of large computer that runs an entire corporation.
• Supercomputer: Itis the biggest, fastest, and most expensive computers on earth.
• Microcomputer: Your personal computer is a microcomputer.
Very Useful (1)
Useful (1)
Not Useful (0)
Sonali Yadav
Friday, Feb 03, 2017 at 10:48Related Search
Please login to your account by completing this form
Reset Your password
Please enter the email address you signed up with and we'll send you a password reset link.
A reset password link has been generated and will be sent to you via email.
You can then follow that link and select a new password.
Completing that action will allow you to reset your password and then you can insert a new one.
Please enter the email address you signed up with and we'll send you a password reset link.
A reset password link has been generated and will be sent to you via email.
You can then follow that link and select a new password.
Completing that action will allow you to reset your password and then you can insert a new one.


comments: